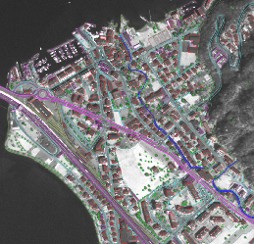
| Article Published on this web site on October 14th 2008 Back to Main Page | ||||||
Remote sensing
is the observation of an object from a distance. Examples are Aerial Photography
and the use of satellites to observe the earth. Remote sensing Systems offer
four basic components to measure and record data about an area of distance.
These components include the energy source, the transmission path, the target
and the satellite sensor. The digital data acquired by the satellites is
transmitted to ground stations and can be used to reconstitute an image of
the Earth’s surface. At Present Ikonas, Quickbird,
Tes, Cartosat are high resolution satellites. Remotely sensed data acquired
by the above earth observation satellites provides a number of benefits
for studying the Earth’s surface, including.
Some examples of uses of satellite data are:
|
The next generation satellites would provide high resolution data. That high resolution images coupled with digital photogrametry for ortho-rectification and GIS contribute to generate large scale maps at good accuracy. The same can be used in upgrading existing maps. References Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation by Lillisand, T.M. and Kiefer T.W., Jhon Wiley. 1999. National Remote sensing agency, India US Geological Survey |
|||||